Bariatric Surgery also known as Weight loss Surgery makes changes to your digestive system either by limiting the amount of food you eat or reducing the absorption of nutrients from food or both, resulting in weight loss.
This Bariatric Surgery Information includes Indications, different types of bariatric surgeries, the risks involved and the benefits of such surgeries.
Indications
Bariatric surgery is an option for weight loss when diet and exercise have not helped or a person has some serious health problem because of being overweight. Generally it is done
- If the Body Mass Index (BMI) is 40 or higher
- Can also be done if the BMI is between 35 and 39.9 plus there are serious weight related health problems such as severe sleep apnoea, heart disease, high blood pressure or type 2 diabetes
A person has to go through extensive screening process before the doctor decides to go for a weight loss surgery. This includes measures to determine whether a person is the right candidate for it or not, moreover it is a very expensive procedure so the expenses should be considered beforehand and of course one has to be fully determined to adapt a very healthy lifestyle permanently to make this type of surgery a success.
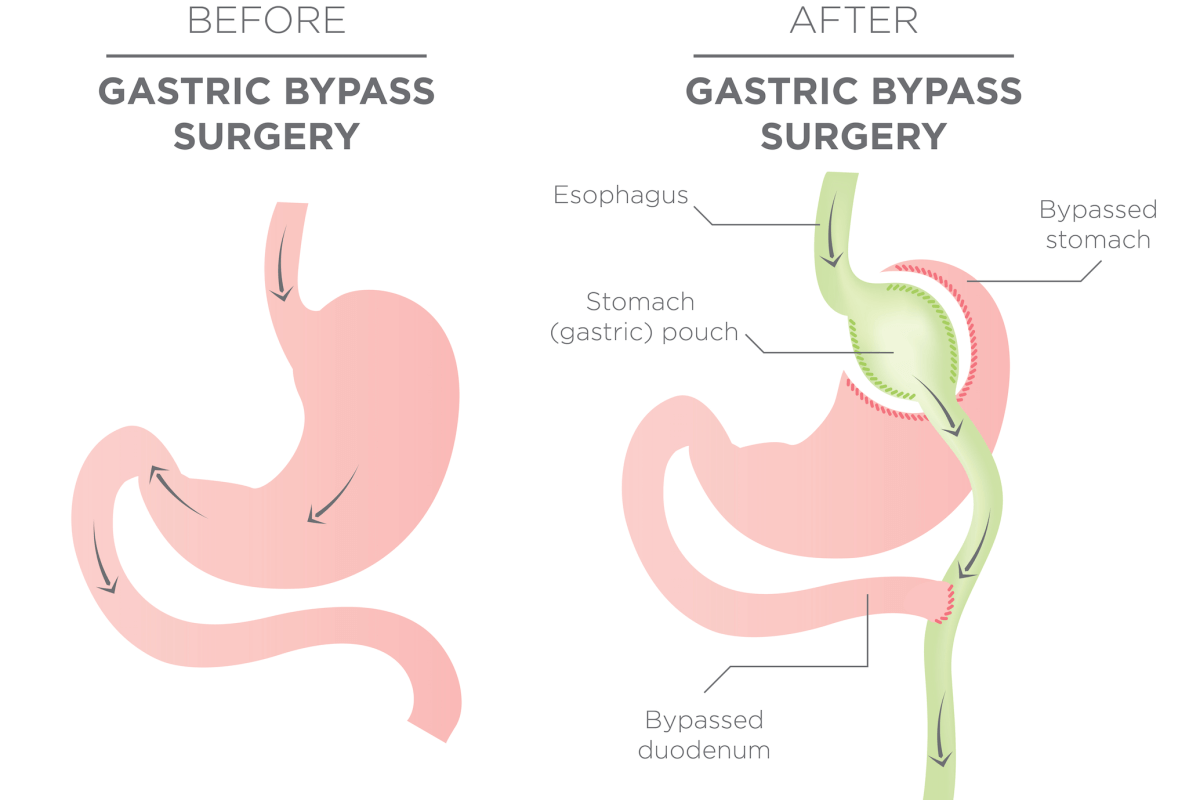
Types of Bariatric Surgery
Roux-en-Y:
This is a type of gastric bypass surgery. It restricts the amount of food you eat at a time as well as reduces the absorption of nutrients released from the food. The stomach is cut across the top sealing it off from the rest making a small pouch and attaching it to a part of the small intestine. The food you eat enters from the pouch into the middle part of the small intestine bypassing the parts where maximum absorption of nutrients takes place.
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch:
Another gastric bypass surgery where almost 80% of stomach is removed. Severe mal-absorption is a problem with this procedure so it is combined with a duodenal switch.
Adjustable Gastric Banding:
A type of restrictive surgery restricting the amount of food you eat. An inflatable band is placed around the uppermost part of the stomach. Inflating the band compresses the stomach dividing into a small upper and larger lower portions communicating via a narrow channel produced by the inflated band. This procedure can be done using a laparoscope.
Stomach Vertical Banding (Stapling): This is a type of restrictive surgery.
Sleeve Gastrectomy with Duodenal Switch:
The stomach is partially resected along its greater curve reducing its volume so restricting food intake. Moreover stomach is detached from the duodenum and reattached to a distant site of small intestine hence reducing the absorption of nutrients taking place in the initial part of the small intestine.
Also Read: When You Shouldn’t ignore Your Back Pains
The type of surgery undertaken depends on many factors and has to be carefully chosen by a specialist.
Diet Changes After Surgery:
A very special diet plan must be followed after the surgery and permanent changes in lifestyle have to be adapted. The diet plan starts from a clear liquid diet to a blended or pureed sugar free diet before a regular diet can be started.
Risks
The risks involved can be due to the surgical procedure itself like excessive bleeding, infection, complications of anaesthesia or they could be long term risks including mal-absorption, bowel obstruction, dumping syndrome causing diarrhoea and vomiting, ulcers, stomach perforation, gall stones, hernias, vomiting and rarely death.
Outcome and Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
Long lasting weight loss is achieved as a result of surgery. How much weight is lost depends on the type of surgery done and the effort put in by an individual to follow the advised changed lifestyle permanently.
In addition to weight loss certain conditions related to excessive weight can be resolved or at least improved by this weight loss surgery. These include heart disease, high blood pressure, severe sleep apnoea, type 2 diabetes and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease.